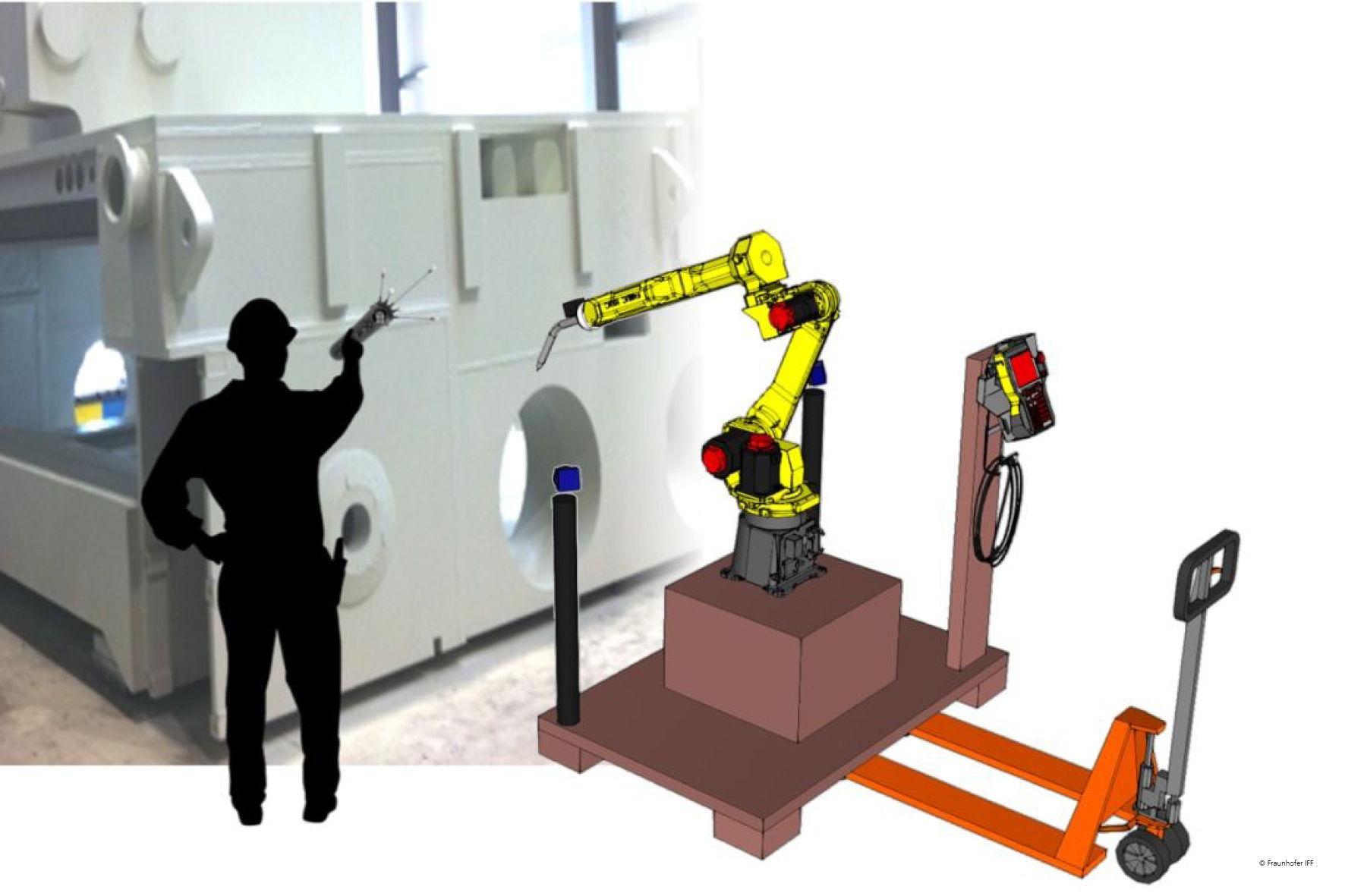
Robot programming for non-experts
In the INTAS project, a development team from Fraunhofer IFF and ATA Anlagentechnik Aschersleben developed and tested intuitive methods of robot programming and motion planning for machining with industrial robots. The project team additionally worked on new control designs that monitor automated welding processes online.
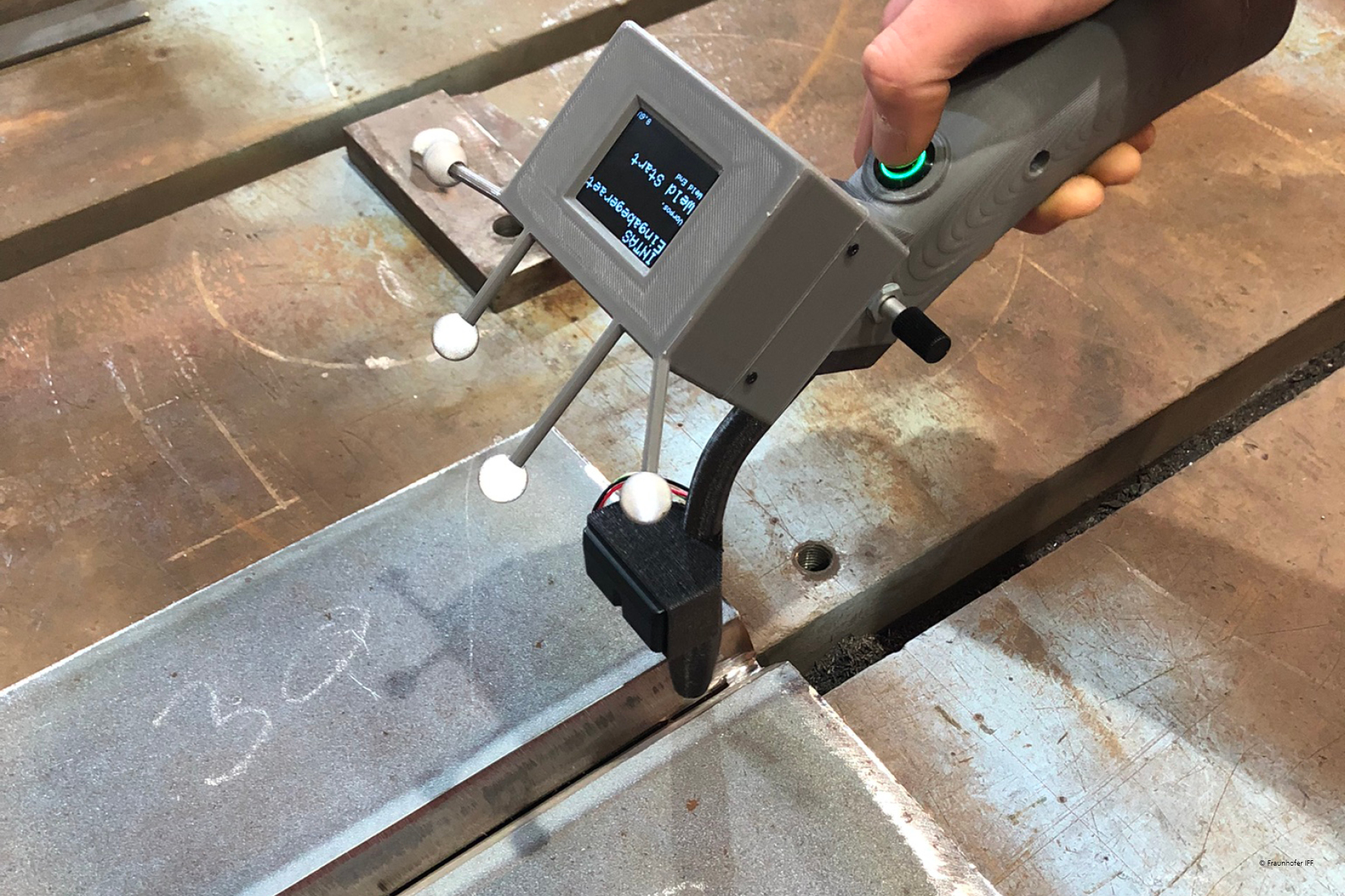
To this end, Fraunhofer IFF’s robotics experts developed an input tool that uses an integrated laser to position the tool. This enables users to define the welding torch’s start and end points very easily and contactless. A background simulation calculates the weld coordinates from the recorded data and scans them for collision points.
At the end of the project, an industrial robot had been produced, which is easily operable and programmable by non-experts, even without extensive knowledge of programming, and can flexibly machine large parts with variable geometries.
Use case: intuitive welding robot programming
In a use case, the new control design was integrated in a welding robot at ATA Anlagentechnik Aschersleben. The welding robot automated hitherto manual welding of heavy and heaviest weldments, freeing welders from monotonous and ergonomically stressful tasks.
INTAS project outcomes
- User-friendly industrial robot that flexibly machines large parts with variable geometries
- Intuitive robot programming without extensive knowledge of programming
- Process monitoring algorithms and routines