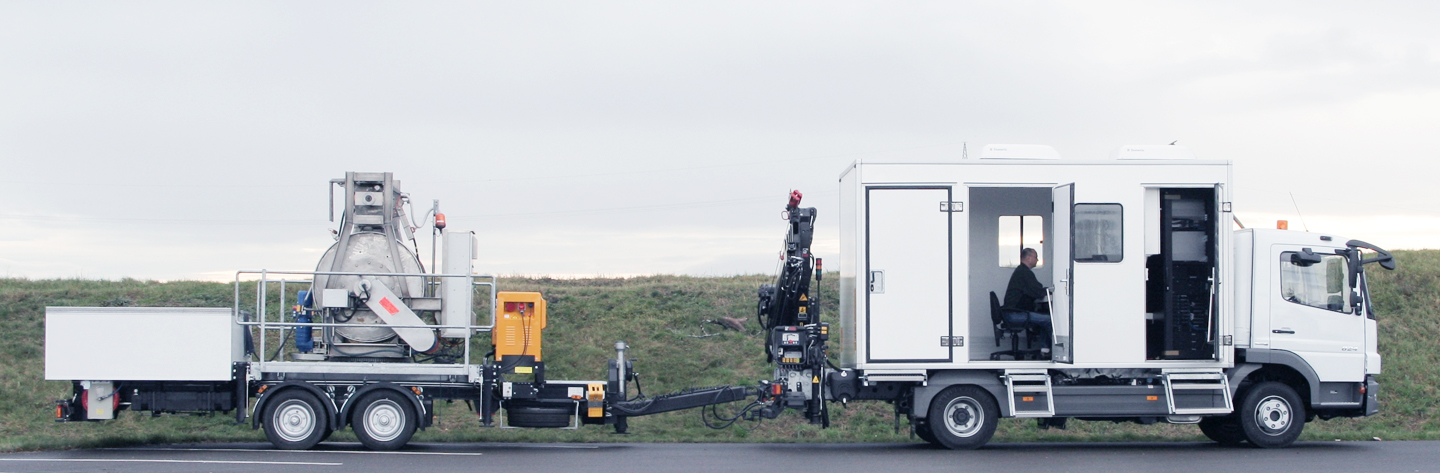
Automated Sewer Inspection
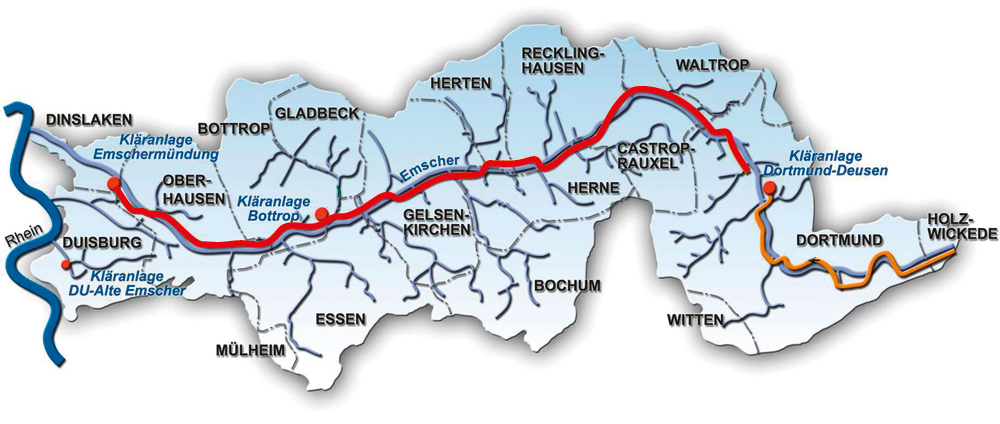
The Emschergenossenschaft has been planning the modernization of its existing above ground sewer system since 1990. In the future, subterranean sewers will drain off sewage and clean water will again flow in the river Emscher. The Emscher sewer system is the heart of this future sewage disposal system. With a total length of 51 km and depths of up to 40 m beneath the surface, the Emscher sewer system is the largest residential water management project in Europe. Pipe diameters are between DN 1600 and DN 2800.